
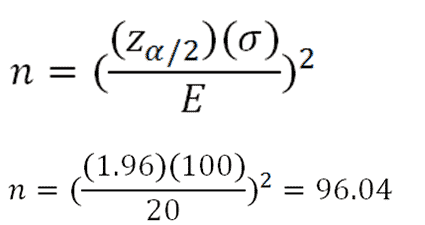
- #TYPES OF STATISTICAL CALCULATIONS FOR SAMPLE SIZE HOW TO#
- #TYPES OF STATISTICAL CALCULATIONS FOR SAMPLE SIZE FREE#
Suppose that you want to survey students at a school which has 6000 pupils enrolled. Choose a number between the minimum and maximum depending on the situation

Sampling more than 1000 people won’t add much to the accuracy given the extra time and money it would cost. This exceeds 1000, so in this case the maximum would be 1000.Įven in a population of 200,000, sampling 1000 people will normally give a fairly accurate result. For example, in a population of 5000, 10% would be 500. A good maximum sample size is usually 10% as long as it does not exceed 1000Ī good maximum sample size is usually around 10% of the population, as long as this does not exceed 1000. If your population is less than 100 then you really need to survey all of them. Most statisticians agree that the minimum sample size to get any kind of meaningful result is 100.
#TYPES OF STATISTICAL CALCULATIONS FOR SAMPLE SIZE HOW TO#
#TYPES OF STATISTICAL CALCULATIONS FOR SAMPLE SIZE FREE#
This article is a short introduction to the topic for a more in-depth coverage of the topic consider enrolling in the free online course offered by University of Florida. For more easy rules of thumb regarding sample sizes for other situations, I highly recommend Sample size: A rough guide by Ronán Conroy and The Survey Research Handbook by Pamela Alreck and Robert Settle. This guide will explain how to choose a sample size for a basic survey without any of the complicated formulas. If this sounds like you, then keep reading. One of the most common questions I get asked by people doing surveys in international development is “how big should my sample size be?”. While there are many sample size calculators and statistical guides available, those who never did statistics at university (or have forgotten it all) may find them intimidating or difficult to use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
